What color tube for troponin – In the realm of cardiac health, troponin levels play a crucial role in assessing heart muscle damage. Understanding what color tube is used for troponin measurement is essential for accurate interpretation of test results. This guide delves into the intricacies of troponin testing, shedding light on its significance and the nuances of blood collection and interpretation.
Troponin, a protein complex found in cardiac muscle cells, is released into the bloodstream when the heart is injured. Measuring troponin levels helps clinicians diagnose and manage conditions such as acute coronary syndrome and heart failure. Proper blood collection techniques are paramount to ensure reliable results, and the choice of tube color varies depending on the specific troponin test being performed.
Definition of Troponin
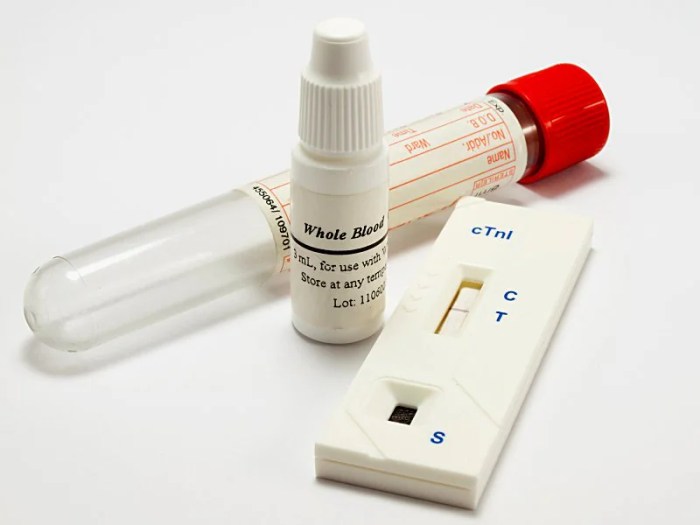
Troponin is a complex of three proteins (troponin C, troponin I, and troponin T) found in the thin filaments of skeletal and cardiac muscle. These proteins play a crucial role in regulating muscle contraction.Troponin is essential for maintaining the proper function of the heart.
When the heart is healthy, troponin levels in the blood are very low. However, if the heart is damaged, troponin is released into the bloodstream. Measuring troponin levels in the blood can help doctors diagnose and assess the severity of heart conditions, such as myocardial infarction (heart attack) and unstable angina.
Role of Troponin in Muscle Contraction
Troponin plays a key role in the process of muscle contraction. When a nerve impulse reaches a muscle, it triggers the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Calcium ions bind to troponin C, which causes a conformational change in the troponin complex.
To test for troponin levels, a healthcare professional may use a lavender-top tube. Incidentally, have you come across the term “used a peeler on crossword”? This phrase has been used in a crossword puzzle . Returning to the topic of troponin, the color of the tube is important for accurate results.
This conformational change allows myosin heads to bind to actin filaments, initiating muscle contraction.
Blood Collection for Troponin Measurement: What Color Tube For Troponin
Accurate blood collection is crucial for reliable troponin measurement. Improper techniques can lead to erroneous results and impact patient management.
Methods for Blood Collection
- Venous Blood Draw:Blood is collected from a vein, typically the antecubital vein in the arm. This is the most common method and is usually performed by a phlebotomist.
- Arterial Blood Draw:Blood is drawn from an artery, such as the radial artery in the wrist. This method is less common and requires more expertise.
Importance of Proper Blood Collection Techniques
Proper blood collection techniques minimize contamination, hemolysis, and clotting, which can affect troponin levels. Key considerations include:
- Using the correct anticoagulant (e.g., EDTA) to prevent clotting.
- Avoiding excessive agitation or shaking of the blood sample.
- Storing the sample at the appropriate temperature.
Troponin Test Interpretation
Troponin test interpretation plays a crucial role in evaluating cardiac events and assessing the risk of myocardial infarction (MI). Understanding the reference ranges and interpreting elevated troponin levels in different clinical scenarios is essential for accurate diagnosis and management.
Reference Ranges
Typical reference ranges for troponin levels vary slightly depending on the specific assay used. Generally, normal troponin levels are:
- Troponin I:< 0.03 ng/mL
- Troponin T:< 0.01 ng/mL
Interpretation of Elevated Troponin Levels
Elevated troponin levels can indicate myocardial injury or damage. The interpretation of elevated troponin levels depends on the clinical context and the timing of the test:
- Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS):Elevated troponin levels in the setting of chest pain or other ACS symptoms are highly suggestive of MI.
- Chronic Coronary Artery Disease (CAD):Elevated troponin levels in patients with known CAD may indicate ongoing myocardial damage or instability.
- Heart Failure:Elevated troponin levels can be a marker of ongoing myocardial damage or impaired ventricular function in heart failure patients.
- Non-Cardiac Conditions:Elevated troponin levels can also occur in non-cardiac conditions, such as sepsis, renal failure, or pulmonary embolism. These conditions must be ruled out before attributing troponin elevation to cardiac events.
Troponin Levels and Cardiac Events
The timing and magnitude of troponin elevation can provide valuable information about the likelihood of cardiac events:
- Early Elevation:Troponin levels that rise rapidly within the first few hours after symptom onset are strongly associated with MI.
- Peak Elevation:The peak troponin level is often reached within 12-24 hours of MI and can indicate the extent of myocardial damage.
- Prolonged Elevation:Troponin levels that remain elevated for more than 24 hours are associated with increased risk of adverse cardiac outcomes.
By considering the reference ranges, clinical context, and timing of troponin elevation, healthcare professionals can accurately interpret troponin test results and make informed decisions about patient management.
Types of Troponin Tests
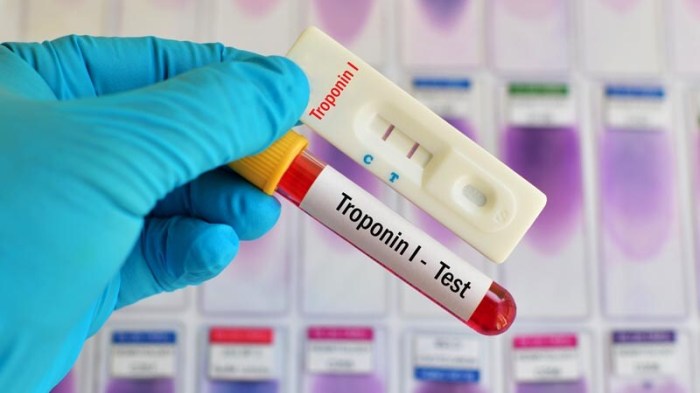
Troponin tests can be categorized into two main types: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative tests detect the presence or absence of troponin in the blood, while quantitative tests measure the specific concentration of troponin. Each type of test has its advantages and disadvantages.
Qualitative Troponin Tests, What color tube for troponin
Qualitative troponin tests are typically used as a screening tool to determine if a patient is likely to have a heart attack. These tests are relatively inexpensive and easy to perform, making them suitable for use in emergency departments and other settings where rapid results are needed.
However, qualitative tests are less sensitive than quantitative tests, meaning that they may not be able to detect low levels of troponin that may be present in patients with early-stage heart attacks.
Quantitative Troponin Tests
Quantitative troponin tests are more sensitive than qualitative tests and can measure the specific concentration of troponin in the blood. This makes them more useful for diagnosing heart attacks and monitoring patients with known heart disease. However, quantitative tests are more expensive and time-consuming to perform than qualitative tests, and they may not be available in all settings.
Clinical Applications of Troponin Testing

Troponin testing is a powerful tool in the clinical diagnosis and management of cardiac conditions. It is particularly useful in diagnosing acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and assessing the risk and prognosis of cardiac patients.
The presence of troponin in the blood indicates myocardial injury or damage. By measuring troponin levels, clinicians can determine the extent and severity of cardiac injury and make appropriate treatment decisions.
Diagnosing Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
ACS is a group of conditions that involve the sudden interruption of blood flow to the heart. Troponin testing is a key diagnostic tool for ACS, as elevated troponin levels are indicative of myocardial injury.
The timing and pattern of troponin elevation can help differentiate between different types of ACS, such as unstable angina, non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Serial troponin measurements over time provide valuable information about the extent and progression of myocardial injury.
Risk Stratification and Prognosis of Cardiac Patients
Troponin testing also plays a crucial role in risk stratification and prognosis of cardiac patients. Elevated troponin levels, even in the absence of ACS, are associated with an increased risk of future cardiac events, such as heart failure and cardiovascular death.
By measuring troponin levels, clinicians can identify patients at high risk and implement appropriate preventive measures, such as lifestyle modifications, medications, or further diagnostic tests.
Examples of Troponin Testing in Clinical Practice
- In the emergency department, troponin testing is used to rapidly diagnose ACS and guide treatment decisions.
- In the intensive care unit, troponin levels are monitored to assess the severity of myocardial injury and guide management of critically ill cardiac patients.
- In outpatient clinics, troponin testing is used to evaluate patients with suspected cardiac conditions and assess their risk of future cardiac events.
Limitations of Troponin Testing
Troponin testing is a valuable tool for diagnosing myocardial infarction (MI), but it is not without limitations. False positives and false negatives can occur, and several factors can affect troponin levels, complicating the interpretation of results.
One limitation of troponin testing is the potential for false positives. Conditions such as renal dysfunction, skeletal muscle injury, and pulmonary embolism can elevate troponin levels, leading to a false-positive diagnosis of MI. Therefore, it is essential to consider the patient’s clinical presentation and other diagnostic tests when interpreting troponin results.
False negatives can also occur with troponin testing. In some cases, troponin levels may not rise significantly enough to be detected by the assay, leading to a false-negative result. This can occur in patients with small or non-obstructive MIs or in those who present late after the onset of symptoms.
Factors Affecting Troponin Levels
Several factors can affect troponin levels, including:
- Renal function: Impaired renal function can lead to elevated troponin levels due to decreased clearance of troponin from the blood.
- Skeletal muscle injury: Trauma, surgery, or other conditions that cause skeletal muscle injury can release troponin into the bloodstream, leading to elevated levels.
- Pulmonary embolism: Pulmonary embolism can cause elevated troponin levels due to right ventricular strain and myocardial ischemia.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of troponin in cardiac health?
Troponin is a protein complex found in cardiac muscle cells. When the heart is injured, troponin is released into the bloodstream, making it a valuable biomarker for assessing heart muscle damage.
Why is proper blood collection important for troponin testing?
Proper blood collection techniques are crucial to ensure accurate troponin levels. Factors such as hemolysis, improper anticoagulation, and contamination can affect the test results.
What are the different types of troponin tests available?
There are various types of troponin tests, including high-sensitivity troponin assays and conventional troponin assays. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of sensitivity, specificity, and turnaround time.