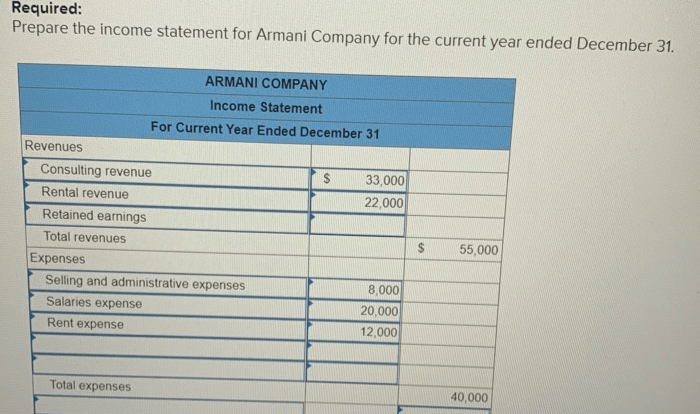
Wang Company accumulates the following adjustment data at December 31, a crucial step in the accounting process that ensures the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. By timely recording these adjustments, companies can correct errors, recognize unrecorded transactions, and align their financial records with the economic reality of their operations.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the significance of adjustment entries, explore various types of adjustments, and discuss their impact on financial statements. We will also provide practical guidance on the procedures for making adjustments and address special considerations for specific accounts.
1. Adjustment Data Accumulation
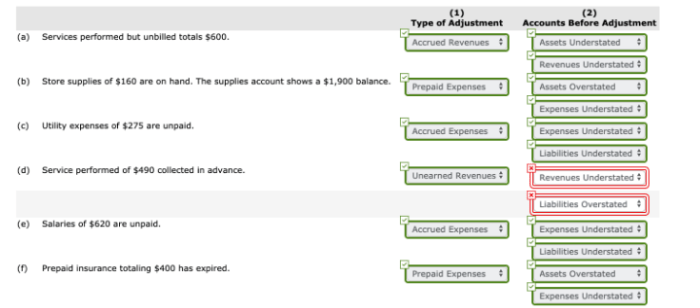
At the end of an accounting period, companies must accumulate adjustment data to ensure the accuracy of their financial statements. Adjustment entries are made to record transactions that have occurred but have not yet been recorded in the accounting system.
These entries are necessary to bring the books up to date and to reflect the true financial position of the company.
Timely adjustment entries are crucial for accurate financial reporting. If adjustments are not made, the financial statements will not reflect the actual financial performance of the company. This can lead to incorrect decisions being made by investors, creditors, and other stakeholders.
Common adjustment entries include:
- Accrued expenses: Expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid.
- Deferred revenues: Revenues that have been received but not yet earned.
- Depreciation expense: The allocation of the cost of a fixed asset over its useful life.
- Bad debt expense: The estimated amount of uncollectible accounts receivable.
2. Types of Adjustments
| Account | Debit | Credit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accrued Expenses | Expense | Liability | To record expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid. |
| Deferred Revenues | Liability | Revenue | To record revenues that have been received but not yet earned. |
| Depreciation Expense | Expense | Accumulated Depreciation | To allocate the cost of a fixed asset over its useful life. |
| Bad Debt Expense | Expense | Allowance for Bad Debts | To estimate the amount of uncollectible accounts receivable. |
3. Impact on Financial Statements: Wang Company Accumulates The Following Adjustment Data At December 31
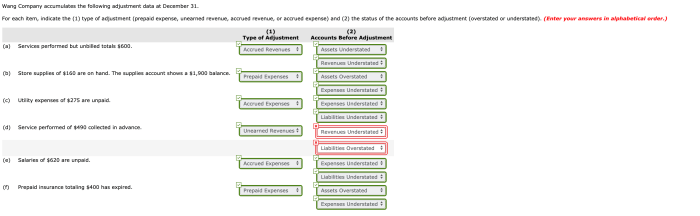
Adjustment entries affect both the balance sheet and the income statement.
On the balance sheet, adjustment entries can:
- Increase or decrease assets.
- Increase or decrease liabilities.
- Increase or decrease equity.
On the income statement, adjustment entries can:
- Increase or decrease revenues.
- Increase or decrease expenses.
- Increase or decrease net income.
Adjusting entries are essential for accurate financial reporting. Without adjusting entries, the financial statements would not reflect the true financial position of the company.
For example, if a company fails to record accrued expenses, the financial statements will overstate the company’s net income. This could lead to investors making incorrect decisions about the company.
4. Procedures for Adjustment
The adjustment process involves the following steps:
- Identify the transactions that need to be adjusted.
- Determine the amount of the adjustment.
- Record the adjustment entry in the accounting system.
To ensure accuracy in adjustment entries, it is important to:
- Use supporting documentation to verify the adjustments.
- Review the adjustments with a supervisor or other qualified individual.
- Use a checklist to ensure that all adjustments have been made.
The trial balance can be used to verify the adjustments. The trial balance should balance after all adjustments have been made.
5. Special Considerations

There are some unique considerations for adjusting entries related to:
- Inventory
- Prepayments
- Unearned revenues
For example, inventory must be adjusted to reflect the cost of goods sold. Prepayments must be adjusted to reflect the amount of the prepaid expense that has been used. Unearned revenues must be adjusted to reflect the amount of the unearned revenue that has been earned.
Q&A
Why are adjustment entries important?
Adjustment entries are important because they correct errors, recognize unrecorded transactions, and align financial records with the economic reality of a company’s operations.
What are the most common types of adjustment entries?
Common types of adjustment entries include accrued expenses, deferred revenues, depreciation expense, and bad debt expense.
How do adjustment entries affect financial statements?
Adjustment entries can affect both the balance sheet and income statement. For example, an adjustment entry to record accrued expenses will increase expenses and decrease liabilities on the balance sheet, while also decreasing net income on the income statement.