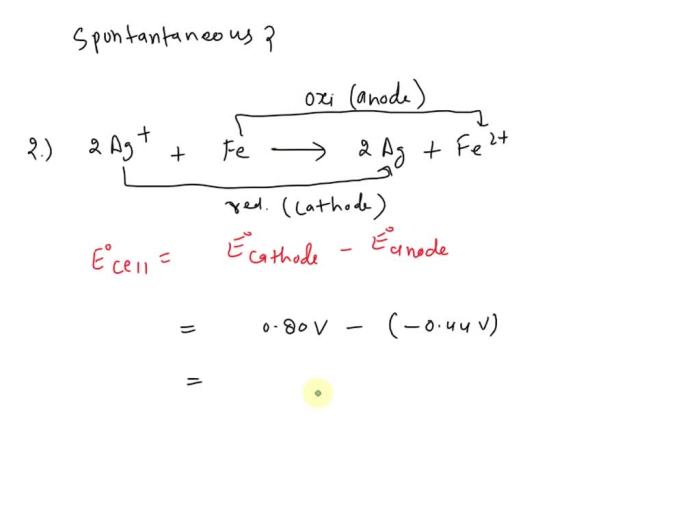
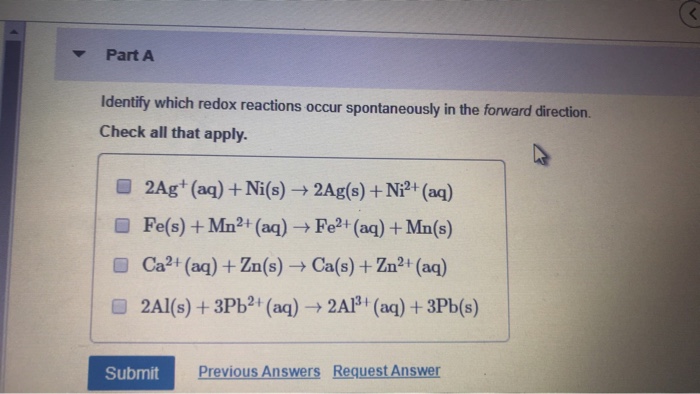
Identify which redox reactions occur spontaneously in the forward direction. – In the realm of chemistry, redox reactions play a crucial role in understanding the transfer of electrons and the spontaneity of chemical processes. This guide delves into the fascinating world of redox reactions, exploring the factors that determine their spontaneity and the methods used to identify those that occur spontaneously in the forward direction.
Redox reactions, characterized by the simultaneous transfer of electrons between reactants, exhibit varying degrees of spontaneity. The concept of spontaneity, a measure of the reaction’s tendency to proceed without external intervention, is central to understanding the behavior of redox reactions.
Factors Affecting Redox Reaction Spontaneity

The spontaneity of a redox reaction is primarily determined by the standard reduction potential (E°). E° is a measure of the tendency of a half-reaction to undergo reduction. A more positive E° indicates a greater tendency for reduction.
The Nernst equation can be used to predict the spontaneity of a redox reaction under non-standard conditions:
E = E°
(RT/nF) ln(Q)
where:
- E is the cell potential under non-standard conditions
- E° is the standard reduction potential
- R is the gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K)
- T is the temperature in Kelvin
- n is the number of electrons transferred in the reaction
- F is the Faraday constant (96,485 C/mol)
- Q is the reaction quotient
If E is positive, the reaction is spontaneous in the forward direction. If E is negative, the reaction is non-spontaneous and will not occur unless an external force is applied.
Methods for Identifying Spontaneous Redox Reactions
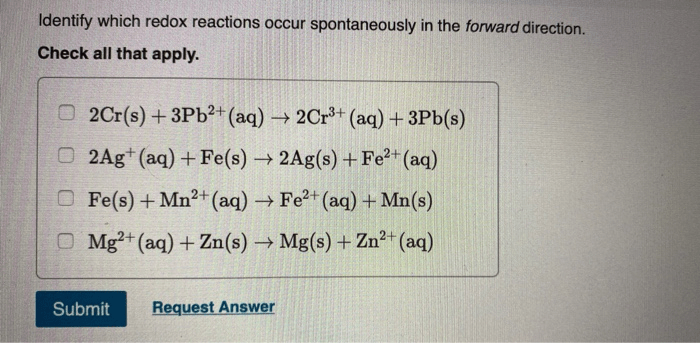
Half-Reaction Method
The half-reaction method involves breaking down the redox reaction into two half-reactions: one for oxidation and one for reduction. The half-reaction with the more positive E° will be the spontaneous half-reaction. If the oxidation half-reaction has a more positive E° than the reduction half-reaction, the overall reaction will be spontaneous.
Electrochemical Series, Identify which redox reactions occur spontaneously in the forward direction.
The electrochemical series is a list of elements arranged in order of their standard reduction potentials. The more positive the E° of an element, the more likely it is to undergo reduction. By comparing the E° values of the reactants and products, it is possible to predict the spontaneity of a redox reaction.
Applications of Spontaneous Redox Reactions
Batteries and Fuel Cells
Spontaneous redox reactions are used in batteries and fuel cells to generate electricity. In a battery, the reactants are stored in separate compartments and the reaction is controlled to produce a steady flow of electrons. In a fuel cell, the reactants are continuously supplied and the reaction is used to generate electricity.
Biological Processes
Spontaneous redox reactions play a vital role in biological processes such as respiration and photosynthesis. In respiration, glucose is oxidized to produce energy, while in photosynthesis, water is reduced to produce oxygen.
FAQs: Identify Which Redox Reactions Occur Spontaneously In The Forward Direction.
What are the key factors that determine the spontaneity of redox reactions?
The standard reduction potential (E°) is a crucial factor in determining the spontaneity of redox reactions. A positive E° value indicates a spontaneous reaction, while a negative E° value suggests a non-spontaneous reaction.
How can we predict the spontaneity of redox reactions using the Nernst equation?
The Nernst equation allows us to calculate the cell potential (E) of a redox reaction under non-standard conditions. A positive E value indicates spontaneity, while a negative E value suggests non-spontaneity.
What is the half-reaction method, and how is it used to identify spontaneous redox reactions?
The half-reaction method involves splitting the redox reaction into two half-reactions (oxidation and reduction) and then balancing them in terms of mass and charge. By comparing the standard reduction potentials of the half-reactions, we can determine the spontaneity of the overall reaction.